In illustrating the Lewis and Clark Expedition, the artists worked within the historical frameworks of their times. Nineteenth century tools and methods utilized engraving, lithography, the physiognotrace, and early photography processes. These pages analyze and illuminate those tools and methods.


At Lewis’s right is Clark’s servant, York, dressed in blue as befitted a personal slave at that time. The Indian squatting at Lewis’s left hand is Toby, the Shoshone guide the captains had hired to lead them across the Bitterroot Mountains toward the Columbia River.
Dyes and Shellac
by Joseph A. Mussulman

A brief account of the dyes and shellacs used at the time of the Lewis and Clark expedition.


After Lewis’s preliminary sketch, later artists and photographers contributed to the visual documentation of the “sublimely grand” waterfall including Barralet, Gustavus Sohon, A. E. Mathews, and F. Jay Haynes.


The story behind Charles M. Russell’s 1912 painting of the expedition meeting the Bitterroot Salish at Ross’ Hole, one of the great works of Western American art.


Because the Shoshone woman has been the subject of so many sculptures and paintings, especially since about 1900, we have a rich heritage of artists’ conceptions to contemplate.
Profile Portraiture
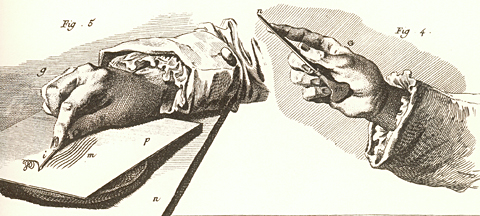
by Joseph A. Mussulman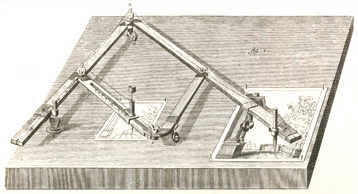

In 1802 the British-born Philadelphian, John Isaac Hawkins (1772-1805)5, invented a new kind of copy machine, a pantograph with which a person could produce a miniature copy of his or her profile through direct contact. He called it a physiognotrace.

The printing of pictures employed a 350-year-old technology based on a process called intaglio—from an Italian word meaning to “cut in”—in which lines and dots were incised into a metal sheet called a plate.


In 1798 a German actor-playwright-turned-printer named Alois Senefelder (1771-1834) discovered the principle of lithography, relying upon simple chemical principles—the mutual repulsion of oil and water, and the mutual attraction of water and salt.
L&C Artists
Interpreters of the trail


Due to the relative paucity of illustrations in the journals, Lewis and Clark storytellers rely on the drawings, paintings, engravings, statuary, and photographs of early travelers and modern interpreters alike. Listed here are early travelers and modern interpreters with indexes of their artwork used on this site.


As documented by Edward Curtis
Photographer Edward Curtis himself described the processes pictured here. “In the preparation of this article of food the salmon was beheaded and gutted, and with a sharp knife the two halves were separated from the backbone and the skin.”


With every crossing they unavoidably drifted farther downstream. Lewis recounted the climactic rafting episode of the day.
Portraits of William Clark
by Joseph A. Mussulman

Four portraits and one statue by five different artists show a diverse interpretation of the likeness of William Clark.


Two hundred years after the event, interpretive artist Michael Haynes explains how he created his painting “Hallowed Ground.”
Experience the Lewis and Clark Trail
The Lewis and Clark Trail Experience—our sister site at lewisandclark.travel—connects the world to people and places on the Lewis and Clark Trail.
Discover More
- The Lewis and Clark Expedition: Day by Day by Gary E. Moulton (University of Nebraska Press, 2018). The story in prose, 14 May 1804–23 September 1806.
- The Lewis and Clark Journals: An American Epic of Discovery (abridged) by Gary E. Moulton (University of Nebraska Press, 2003). Selected journal excerpts, 14 May 1804–23 September 1806.
- The Lewis and Clark Journals. by Gary E. Moulton (University of Nebraska Press, 1983–2001). The complete story in 13 volumes.

